A bony bump that forms on the joint situated at the base of the big toe is called a bunion.
Bunions are formed when the big toe pushes against the next toe and forces the joints found in the big toe to get bigger and stick out.
Depending on the severity, treatment approach can range from conservative options to bunions surgery.
What causes bunions?
Bunions may develop secondary to inherited structural defects. It may also be caused by wearing narrow and tight shoes. Its development can also be attributed to other medical conditions like arthritis.
Other factors like excessively flexible ligaments, flat feet, and abnormal bone structure have been known to also contribute to the development of bunions.
What are the prevalent symptoms of bunions?
Apart from the noticeable bump, other indicators of bunions may include:
- Inflammation and redness of the skin on the affected area
- Thick skin manifesting on the big toe’s underside
- Development of calluses on the second toe
- Pain that can be persistent or may come and go
- Difficulty when moving the big toe
What are the possible complications?
While bunions do not always cause problems, the condition becomes permanent unless corrected through bunions surgery.
Likely complications when left untreated can include:
- Hammertoe – this condition is characterized by an abnormal bent that manifests in the toe’s middle joint (typically, the one next to the big toe) and can cause pressure and pain.
- Bursitis – this condition occurs when the bursae (small fluid-filled pads) that cushion the tendons, bones, and muscles are inflamed.
- Metatarsalgia – this condition causes inflammation and pain to the ball of the foot.
How do you prepare for your appointment?
When visiting a podiatrist or an orthopedic foot specialist, preparing a list of questions would be ideal so you can make the most out of your visit.
For starters, the following key questions should make it to your list:
- What are the causes of the condition?
- Is the condition going to be temporary or permanent?
- What treatment approach is ideal?
- Am I a likely candidate for bunions surgery?
Your doctor will also have questions for you so make sure you have the answers ready prior to your visit.
Some of the likely questions your doctor will ask include:
- When did you start noticing the symptoms?
- Is the pain severe?
- What type of shoes do you wear?
- Is there anything that seems to improve your symptoms?
- Is there anything that seems to worsen your symptoms?
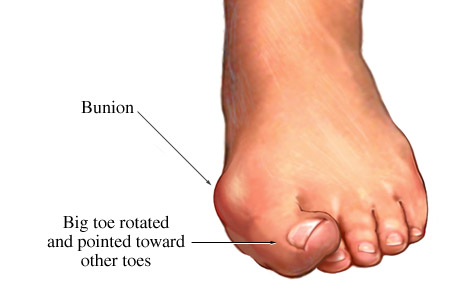
What are the treatment options for bunions?
Conservative treatment options
Nonsurgical treatment alternatives that can help relieve pressure and pain can include:
- Taping, padding, or splinting – your doctor can pad or tape the foot in a normal position to help minimize stress and ease the pain.
- Medications – ibuprofen (Motrin IB, Advil), naproxen (Aleve), and acetaminophen (Tylenol) can help control bunion pain. Cortisone injections are also considered helpful.
- Applying ice – icing the bunion can relieve both inflammation and soreness.
- Shoe inserts – padded shoe inserts can help evenly distribute pressure especially when you are on the move. OTC arch supports may also provide relief albeit others may need prescription orthotic devices.
Surgical options
If the condition does not respond to conservative and noninvasive alternatives, bunions surgery may be recommended.
Surgical procedures for bunions may entail:
- Straightening the big toe (done by removing a part of the bone)
- Removing the tissue that is swollen
- Realigning the long bone
- Joining the bones permanently
Generally, surgery is often only recommended when the condition causes severe (and frequent) pain and begins to interfere with your day-to-day routine.